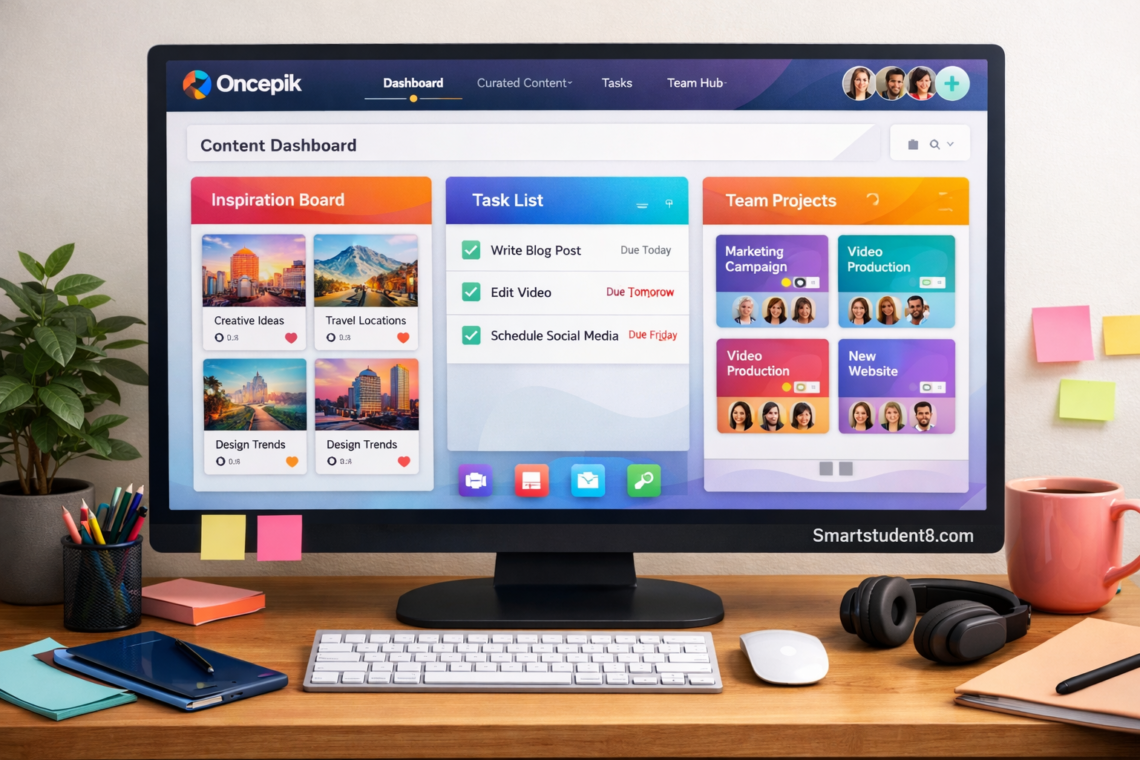
In an environment filled with countless applications and tools that are countless, it can be difficult to manage information. Links are lost, ideas get scattered on different notes, and projects in teams become unorganized. Oncepik is a solution that integrates content curation with project management and team collaboration in a single intuitive platform. This platform provides a unified workspace for individuals or teams to organize their digital assets, keep track of tasks, and easily communicate. The platform was designed for those who want to organize their digital life, enhance productivity, and increase creativity.
It does this without having to juggle multiple tools. Oncepik’s visual approach helps turn abstract ideas into real projects and simplifies complicated workflows. This guide offers a comprehensive exploration of the Oncepik Platform. This guide will explore its key functionalities, from powerful content management features to real-time collaborative tools. Learn how the unique task management approach can increase productivity in small and large teams alike.
In addition, we will explore specific use cases to show how professionals from various industries can use the platform. Once you understand the benefits of Oncepik and its practical applications, it will be clear why this tool is different from others and how it can help to improve your digital workflow.
Oncepik: The Core Concept
Oncepik is a digital platform with many features and functions designed to help simplify modern personal and work organization. The platform is an all-in-one hub that allows users to collect and organize digital content. Users can also manage projects and tasks, as well as collaborate in real-time with other people. Oncepik, unlike single-purpose apps that only focus on one aspect, integrates multiple workflows in a visually driven, unified environment. It is the central goal of the platform to eliminate the frustration that can be caused by switching from one app to another for bookmarking, task management, or file sharing. This platform creates an integrated space that allows ideas to be developed and implemented without interruption. The approach allows users to maintain their focus and makes sure that all important information can be accessed and contextualized in the context of their larger projects.
The platform is built around the idea that visual organizing enhances comprehension and increases creativity. Oncepik uses visual boards and drag-and-drop interfaces to replace the traditional folders and lists that are heavy on text. Users can see the big picture, learn about relationships, and organize their projects in ways that make sense. Oncepik allows you to customize your workspace according to the way that you work, whether it’s a planner of a social-media calendar, an organizer for research material, or even a manager who oversees a team. Its focus on visuals and a user experience makes it stand out as a great tool for those who want to streamline their digital tasks.
Advanced Content Curation: Streamlining Digital Workflows
Oncepik’s ability to automate content curation, knowledge management, and other aspects is one of its most important features. Professionals and students are constantly gathering articles, videos, and images from the internet in an age of information overload. Oncepik is a powerful tool for organizing and capturing this information. Users can add links to project boards with just a click using the browser extension. They can also categorize them and tag them. The process is more than just bookmarking, as it allows users to make notes, highlight important passages, and link saved content to tasks within their workspace. The integration transforms scattered research into an organized and useful knowledge base.
Content organization tools on the platform are available for individual or collaborative use. For example, a marketing team can curate content such as industry news, analysis of competitors, or inspirational material for an upcoming project using a shared board. The visual design makes it simple to view all of the materials collected. Each team member can add links and resources. The collaborative nature of the project ensures that everyone has access to the same information. This helps reduce redundant efforts and promotes alignment. Once. Pik is a great tool for individuals to use as their personal library. This can be used to support learning, hobbies, or professional development. You can create dedicated boards to support your interests and goals by creating a searchable knowledge base.
Enhancing team productivity through collaboration tools
Oncepik facilitates seamless teamwork, regardless of location. The platform offers real-time features for collaboration that keep everyone in sync and on track with project goals. Team members can collaborate on shared workspaces, which allow them to see real-time updates when tasks, documents, and comments are updated. The transparency of the shared workspaces eliminates the need to hold constant meetings for status updates and long email chains. All relevant information is centralized in the context of the project. This platform allows users to comment directly on the tasks they are working on, to attach documents, to discuss their ideas, etc. It creates an organized and clear record of communications, which reduces miscommunications while ensuring everyone is up-to-date.
Oncepik’s collaborative platform was designed to be flexible. It can accommodate different team sizes and types of projects. Assign tasks to team members and set deadlines. Track progress at different stages in a workflow. The level of organisation ensures accountability and allows managers to monitor the health of a project without micromanaging. The visual aspect of the boards can serve as a whiteboard digital for creative teams to brainstorm ideas, arrange them, discuss, and refine them. File-sharing features on the platform allow easy sharing of images, documents, and other project assets. Oncepik’s integrated tools foster a cohesive, productive, and efficient team environment.
Oncepik Task Management: A deep dive into the Features
Oncepik’s core is a task and project management software that allows users to turn their plans into reality. The tool goes beyond a to-do list by providing a visual and dynamic way of managing workflows. The user can break down tasks into subtasks and then organize them in customizable boards. These can be tailored to suit methodologies such as Kanban or customized project stages. The details of each task, such as the due date, priority level, attachments, and notes, can provide a complete overview. The level of detail allows individuals and groups to work confidently and with confidence, as all the necessary information will be readily accessible.
Its task-management system was also created to boost personal productivity. Oncepik can be used to track goals, manage daily schedules, and plan projects. Visual interfaces can help users to prioritize and track their work, which is highly motivating. The ability for teams to monitor and assign tasks in real-time is of great value. Project managers have the option to get an overview of the project or dig into specific tasks in order to find bottlenecks. They can also reallocate their resources if necessary. Automated features such as creating templates or recurring tasks for common projects streamline workflows, saving time and reducing administrative workload. Oncepik’s robust features make it a flexible solution to manage tasks for both individual users and complex team projects.
How Oncepik Boosts Creativity and Idea Generation
Oncepik offers more than just an organization tool; it’s also a platform that fosters creativity and innovation. The flexible visual workspace allows users to break free from the constraints of documents and lists. Drag-and-drop allows users to arrange ideas in a free-form manner, including images, notes, links, and other elements. This creates a canvas that can be used for mind mapping and brainstorming. The unstructured nature of this environment makes it ideal for early creative stages, when the aim is to experiment with ideas without making premature judgements. The board can be used by a writer to create an outline of a story. A designer can make a moodboard with images for inspiration. And a team from marketing can come up with campaign slogans.
Content curation is another way the platform enhances creativity. Users can develop new ideas by identifying patterns and making connections when they organize inspiration visually. It is incredibly powerful to be able to gather all of your inspiration and research in one location. Oncepik also includes community discovery feeds and gamified features that encourage users to engage with the platform. Users can then browse through ideas and templates from other users. Exposure to other approaches and solutions may spark fresh insights, and even help break through creative blocks. Oncepik provides tools to support divergent and convergent thought processes, such as brainstorming or planning.
Compare Oncepik with Traditional Productivity Platforms
It is important to know how Oncepik compares with other productivity platforms such as Asana, Trello, and Notion. Although tools such as Trello or Asana can be excellent for project and task management, their focus is often on structured workflows. They may not provide the same flexibility when it comes to content curation and brainstorming. Oncepik has integrated these features directly into the project workflows. Users can manage their tasks along with research and creative assets, without having to switch applications. The all-in-one approach allows for a holistic view of the project. Background research is combined with the tasks that can be executed in the same application.
Oncepik is more engaging and visually dynamic than Notion. Notion has powerful database and knowledge management features. Notion is text-heavy, static, and can be difficult to use. Oncepik, on the other hand, has a focus on interactive boards and layouts as well as gamified features. This makes it an ideal choice for teams and creative workflows that rely on visual collaboration. Its mission is to combine task management, digital organization, and creative expression into one cohesive ecosystem. This is more than just a bookmarking tool or project management software. It’s a complete productivity hub that can adapt to all the needs of users today, whether they are freelancers, large teams, or corporate employees.
The Practical Use Cases of Professionals and Teams
Oncepik is a versatile tool that can be used in a variety of roles and industries. The platform is a great tool for marketing professionals to plan campaigns. The team can use a board for managing a content schedule, to brainstorm, to curate ideas, and to track progress from conception until publication. Each task can be accompanied by design mockups and copy drafts. Performance analytics are also available. This keeps everyone informed and in sync. The centralization of campaign assets and communications streamlines the marketing workflow.
Oncepik is a great tool for creative professionals like writers, designers, and content creators to organize and manage projects. Graphic designers can create a library that includes design trends, client feedback, and color palettes. These are all connected to project boards. It helps to maintain a cohesive creative vision, and all reference materials will be readily available. Oncepik can be used by students, educators, and parents to organize research, plan study schedules, and collaborate on group projects. Students can save relevant articles, lecture notes, and assignment details on boards created for specific courses. The level of organisation can improve the learning outcome and decrease stress associated with managing academic obligations. The examples above show how Oncepik can adapt to the needs of each user and be an asset in enhancing productivity.
Get Started to Maximize Your Experience
Oncepik’s intuitive user interface makes it easy to get started. Start with one specific project. Focusing on a single goal, whether it is planning your personal trip, organizing work for the coming week, or starting a team initiative,e will allow you to learn about the core features of the platform in an actual context. Use the templates to plan projects, create content calendars, or have brainstorming sessions. You can easily customize these pre-built boards to meet your needs. This will save you time and help you become more organized. Once you are comfortable with the system, you can create your own templates to help you organize recurring tasks.
It is important to embrace the organizational tools of your platform in order to get the most out of it. You can categorize bookmarks, notes, and tasks using tags and folders. This will help you find the information more easily. Assign roles and responsibilities to each task in team projects to make sure everyone understands their responsibilities. Review your boards regularly to clear out completed projects and declutter them. This will help you maintain an organized and focused workspace. Oncepik can help you transform your workflow, eliminate clutter,r and increase productivity by integrating it into your daily life and using its tools to organize your tasks and information.
Read More: Gaming Tips PBLinuxTech: Your Ultimate Guide to Peak Performance
Conclusion
Oncepik is a unique solution to organize, manage, and collaborate on digital content. We’ve shown how the visual approach to content curation, flexible task management, and powerful tools can help individuals and groups simplify their work. Oncepik’s centralization of project assets eased collaboration and creativity fosters users to cut through digital clutter.
Oncepik offers tools that will help you achieve your goals, whether you’re a professional creative looking for inspiration or a leader of a large team overseeing numerous projects. The intuitive user interface makes it simple to adapt your workspace to meet your needs.
Explore Oncepik if you want to increase your productivity, promote creative thinking, and have all of your digital files in one place. Experience a new, more collaborative and inspirational way of working. This approach is built to keep up with the speed and possibilities in today’s digital age.